Key Points:
<aside> 💡 Remote sensing can be defined as the detection and monitoring of physical and geospatial data of a given area through measuring reflected and emitted radiation at a distance, utilizing satellite information.
</aside>
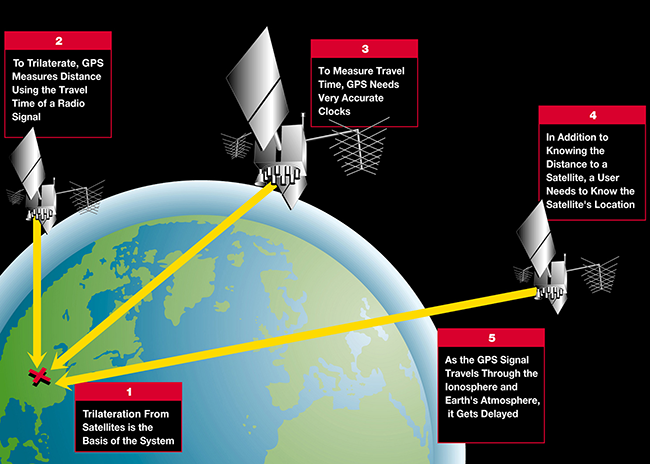
A GNSS is a constellation of satellites that determine locations by providing signals from space that transmit positioning and timing data to receivers. The process utilizes triangulation, in which a receiver on Earth calculates the amount of time taken by radio signals to travel from four or more satellites to its location. Then by calculating the distance to each satellite, the receiver can determine the user’s longitude, latitude, and altitude. The receiver must also calculate current velocity through measuring the Doppler effect shifts in signals.

Triangulation of GNSS
The performance of GNSS can be assessed through four criteria of accuracy, integrity, continuity, and availability.

Criteria defined by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme
This was the critical technology behind the Cold War-era competition between the United States’ GPS and the Soviet Union’s GLONASS systems. Since then, alternative GNSS have been developed and launched by China, the European Union, and Japan, with distant plans by South Korea to launch its own satellite navigation system by 2034.
Satellite imagery reveals visual data via captured information using two broad categories of imaging sensors. Passive sensor satellites collect solar electromagnetic radiation data reflected off of Earth’s surface. In contrast, active sensor satellites emit their own radiation, which is analyzed as it reflects back from Earth. Different sensors will have a certain spatial resolution that determine how much area is able to be captured or the resolution of images. GEO satellites are the primary source of satellite imagery for tracking data such as real-time weather monitoring. These two capabilities, GNSS and satellite imagery, comprise remote sensing and the political implications that can be attributed to satellite technology.
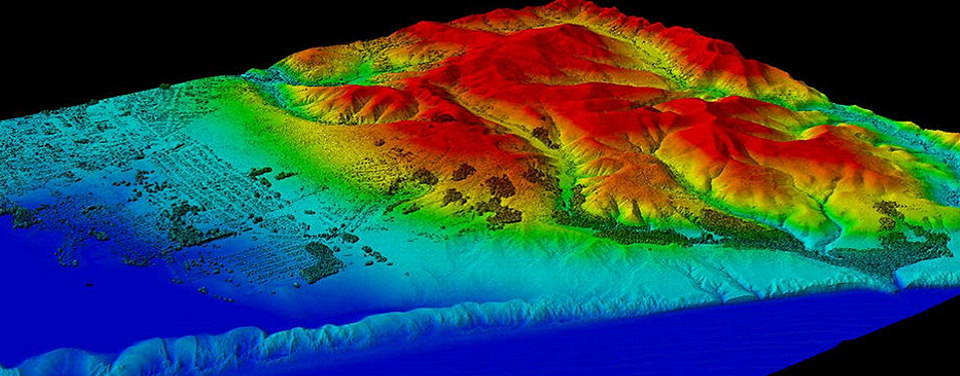
Light Detection and Ranging image created with remote sensing data collected by NOAA's National Geodetic Survey.
Sources:
Logsdon, Tom S. "GPS." Encyclopædia Britannica. April 21, 2021. Accessed June 18, 2021. https://www.britannica.com/technology/GPS
https://www.euspa.europa.eu/european-space/eu-space-programme/what-gnss